Valve End Connection Types
According to valve end connection types, valves may be classified as: flanged end valves; welded end valves; threaded end valves; and hub end valves. Valves with all these end connections are available.
Flanged End:
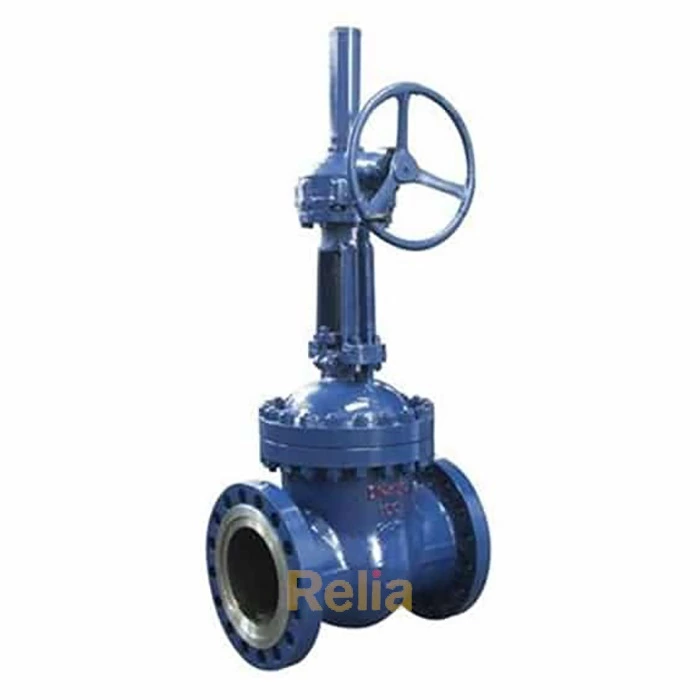
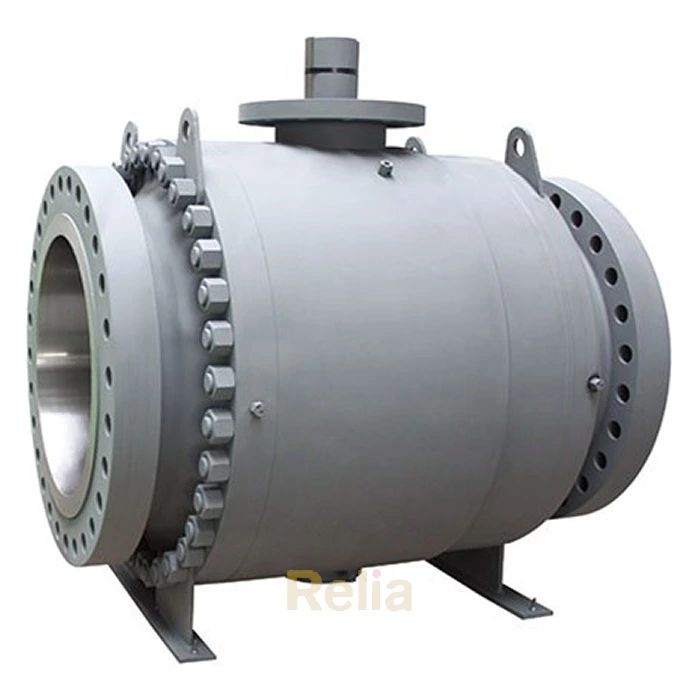
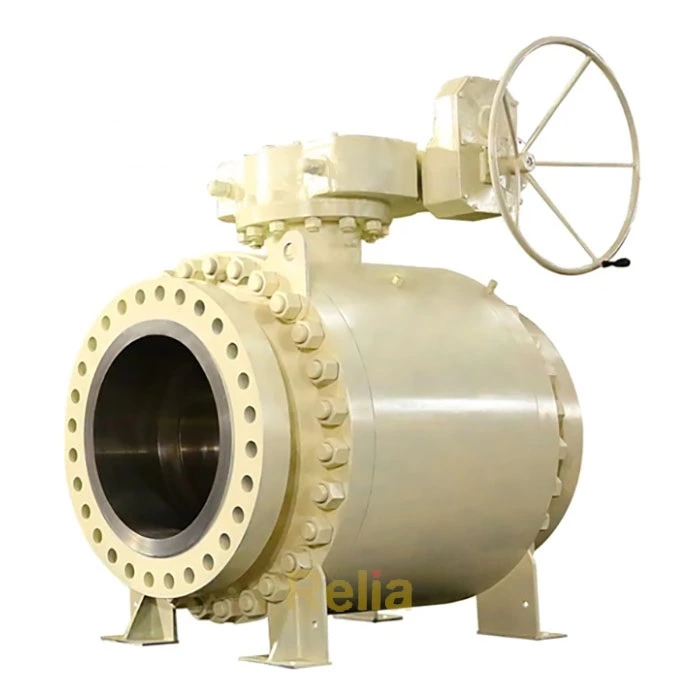
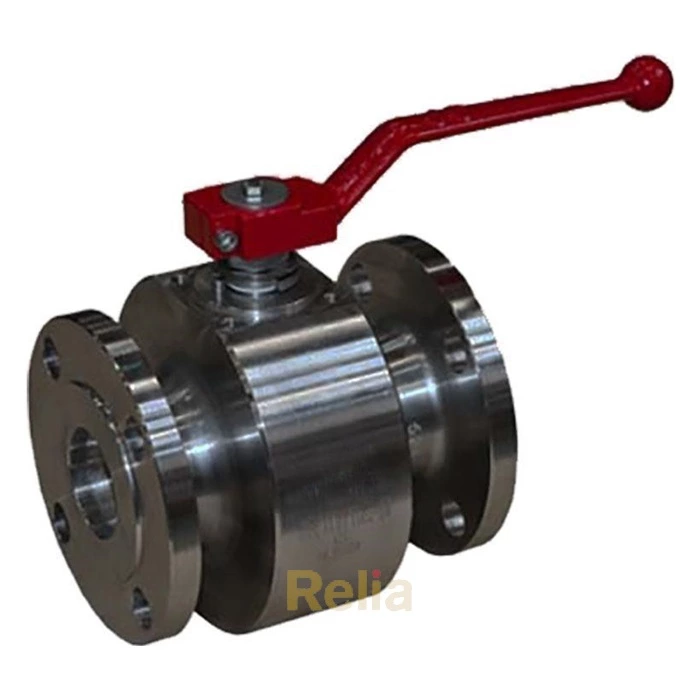
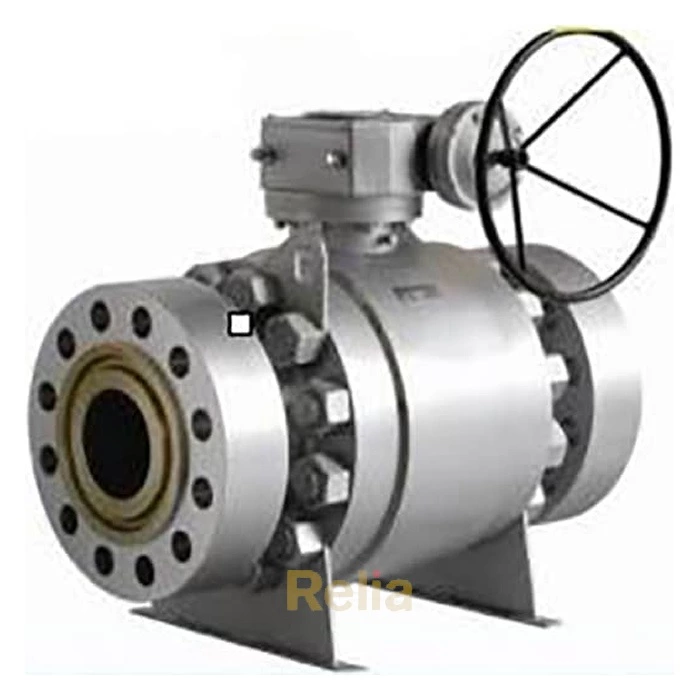
Flanged end connections are in the shape of a flange, and the two flanges are connected using bolts and nuts. Flanged connections are the most common method of connecting valves, regardless of the pressure level (from low to high pressure levels) and valve size (from small to large valves).
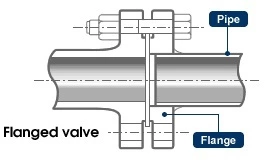
Flanged valves are quite easy to install and can be easily removed for cleaning and maintenance without affecting other parts of the pipe network.
The flanges are solid metal plates with holes through which bolts and nuts are placed to tighten the valve to the pipe. Flanged connections follow strict standards for the parameters. The design of the plates, hole size, hole thread, and hole position are some of the parameters that are set by these standards: ANSI/ASME B16.5, ANSI/ASME B16.47, and DIN 1092-1.
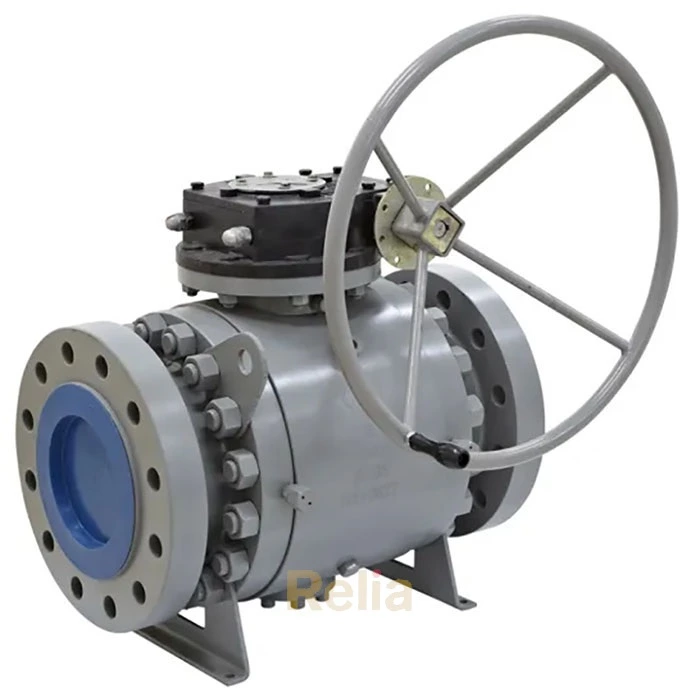

Relia Flanged End Connection Ball Valve
Types of Flange Faces are Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), Ring-Type Joint (RTJ), Tongue-and-Groove (T & G), Male-and-Female (M & F),etc.
Weld End
The valve is welded directly to the pipe. This connection is usually used where perfect shutoff of leakage is crucial, for example, in high-temperature and high-pressure pipeline systems. There are two types of weld: socket weld and butt-weld.
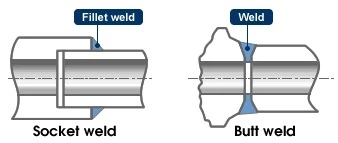
Socket Weld End
The welded end of the valve is formed in the shape of a socket, into which the pipe is inserted and then welded to the valve. This connection is used primarily for small valves, not exceeding 2 inches.
Butt Weld End
The valve and pipe ends are abutted to each other and then welded to form the connection. The two butt edges are beveled for jointing. This connection method can be used for valves of any size.
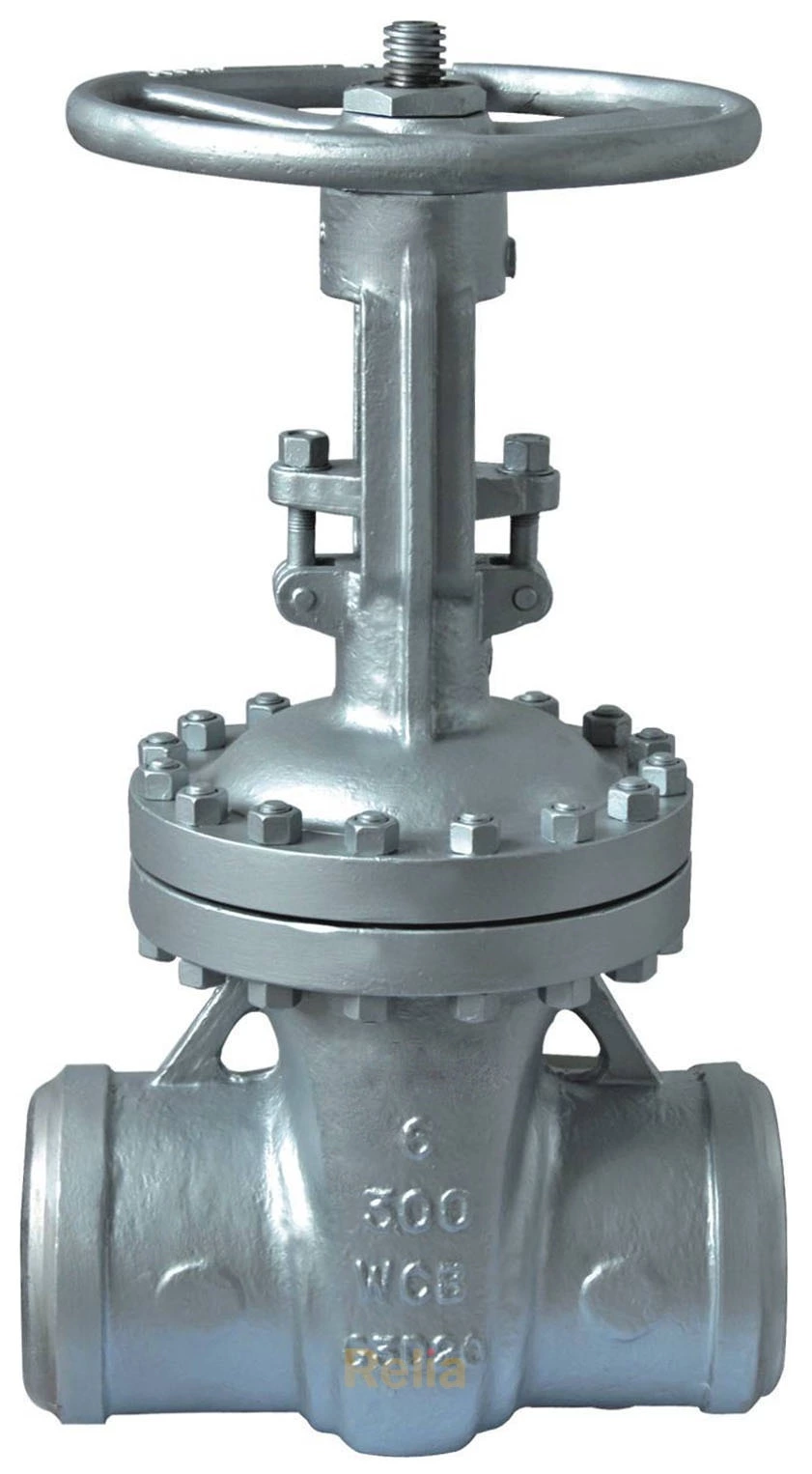

Relia Butt Weld End Gate Valve
Threaded (Screwed) End
The valve is connected to the pipe using pipe threads. This connection type is used primarily for relatively small valves, not exceeding 2 inches with a pressure level of 1 MPa or lower. Unlike other connection methods, the threaded type does not require small parts (bolts and nuts, etc.), making it economical. However, this type of connection is difficult to repair. There are two types of threading: internal and external threads, and tapered and parallel threads. Most valves employ the tapered thread type.
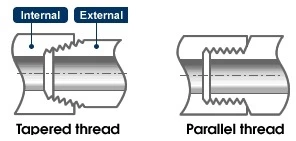
Thread ends are usually NPT (ANSI/ASME B1.20.1) or BSP (ISO 7 and/or EN 10226-1, BS 21).
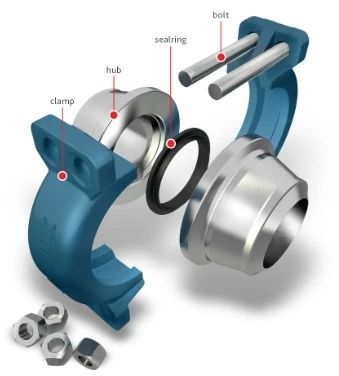
Hub end connection
Hub connections are used for connecting pipe spool joints to each other or other equipment, where weight is a major design criteria. Hub End Valves are lighter, which saves weight and money as compared to flanged end valves. Clamp connection ensures proper clamping force, resulting in no leakage during bending and vibrations, which generally occur in long pipelines.
The Hub Clamp is generally selected by the customer due to the proprietary design of Techlok, Grayloc, and Vector Hub Clam.
The clamp and hub connector joint consists of the following components:
- Two hubs
- Two clamps
- One seal ring
- Eight nuts
- Four studs
Refer to the diagram below that shows the elements of a typical clamp and hub connector.