Automatic Body Cavity Relief In Ball Valves
Automatic cavity pressure relief is provided to relieve the trapped fluid into the internal pipeline, when the ball valve is closed with the fluid trapped in the body cavity and the pressure of the trapped fluid goes up abnormally as the unstable factor. Automatic cavity pressure relief is also called self-relieving seat in a ball valve.
When the valve is closed, the fluid is trapped in the body cavity of a ball valve. As an unstable factor, such as the rise in temperature, the trapped pressure will rise abnormally. It is harmful to the pipeline and may lead to serious risks.
As specified by API 6D, the body cavity pressure shall not exceed 1.33 times the valve pressure rating at the specified maximum operating temperature.
Cavity Relief in Trunnion Ball Valves
A trunnion mounted ball valve with single piston effect seats (SPE) design has an automatic pressure release into the pipeline. It uses "self-relieving seats" to release this pressure.
Body cavity Relief trunnion ball valve
The trunnion-mounted ball valve also traps the media in the body cavity when the operator closes the valve. The pressure in the body cavity increases when heated and pushes the downstream ball valve seat away from the ball by rising pressure against the spring load. When this happens, the pressure gets released.
Cavity Relief in Floating Ball Valves
There are two ways of making cavity relief for floating ball valves.
1. Make a hole through the body cavity to access the valve port (bypass), so the body cavity and the port are at the same pressure condition when the valve is fully closed.
2. In the case of increased temperature, valve position is "full open" and fluid pressurizing direction "1-way".
1). Make a relief groove on the upstream side of the ball seat.
2). Cut a hole in the ball face on the upstream side of the port pass.
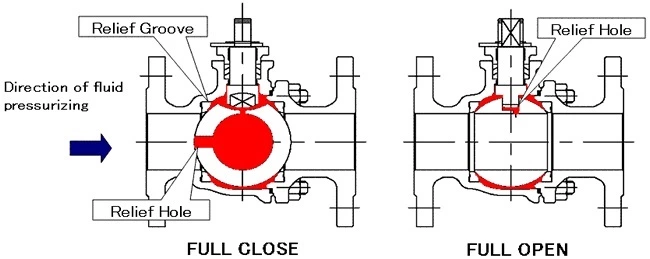
Automatic cavity pressure relief floating ball valve
Cavity Relief Testing For Valves
Cavity relief testing can be performed to detect liquids or other fluids with thermal capacity trapped in the body cavity. Cavity relief testing is recommended where the medium is subject to heating or big differences in temperature between day and night with the potential generation of overpressure in the body cavity with potential hazard for the whole system.
The follinwg is the cavity relief testing specified by API 6D.
B.8 Cavity relief testing
B.8.1 Frequency Each valve shall be tested. Cavity relief testing is not required if protection of the cavity against over-pressure is ensured, for both the open and the closed position, by a hole in the obturator or around the seat seal.
B.8.2 Trunnion-mounted ball valves and through-conduit gate valves with internal relieving seats
The following is the procedure for cavity-relief testing of trunnion-mounted ball valves and through-conduit gate valves with internal-relieving seats.
Fill the valve in the half-open position with water. Close the valve and allow water to overflow from the test connection at each end of the valve. Apply pressure to the valve cavity until one seat relieves the cavity pressure into the valve end; record this pressure relief.
For valve types with second-seat relief, continue to increase the pressure to the cavity until the second seat relieves; record the relief pressure of the second seat. Failure to relieve at a pressure less than 1,33 times the valve pressure rating shall be cause for rejection.
B.8.3 Floating-ball valves
The following is the procedure for cavity-relief testing of floating-ball valves.
With the valve half-open, pressurize the valve to 1,33 times the valve pressure rating specified in 7.2 for the material at 38 °C (100 °F).
b) Close the valve and allow each end to return to atmospheric pressure.
c) Open the valve to the half-open position and monitor for the release of test medium trapped in the cavity. The presence of trapped pressurizing medium in the cavity is grounds for rejection.




