Fire Safe Design in Ball Valves
What Is a Fire-Safe Ball Valve?
Fire-safe ball valves are capable of maintaining their pressure-holding capacity during and for an expected period of time after a fire. These ball valves are typically used in situations where hazardous or flammable liquids are likely to leak from the valve in the event of a fire.
How to Make a Ball Valve Fire Safe?
The use of fire-resistant components is the most common way to make a ball valve fire-safe. They are achieved by using secondary metal seats, graphite gaskets between the body and bonnet, and graphite packings on the valve stem.
The primary goal of fire safety is to prevent both internal and external leakage.
Internal Leakage Prevention
The internal leakage is to be avoided by providing a secondary metal-to-metal seat seal when the soft seat is destroyed by fire.
Floating ball valve
The fire-safe design of floating ball valve is in accordance with API 607 and API SPEC 6FA standards. When non-metallic resilient seats are destroyed in a fire, the ball is pushed onto the downstream metal seat lip, cutting off the line fluid and preventing internal leakage due to a secondary metal-to-metal seal.
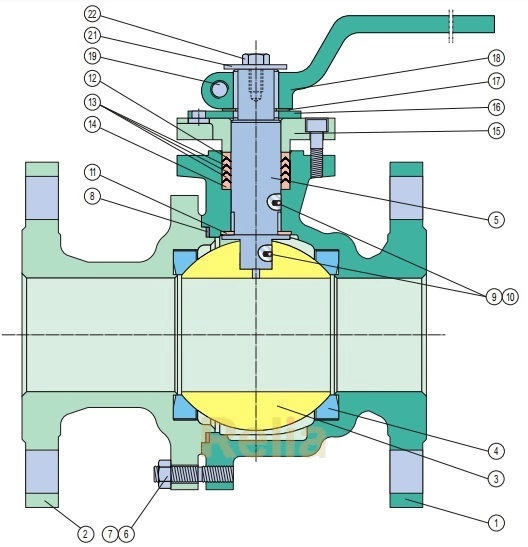
Fire Safe Design Floating Ball Valve with Secondary Metal-to-Metal Seat
Trunnion ball valve
For trunnion ball valves, When fire burned out the primary O-ring seal between the floating seat ring and adapter, also the seat insert between seat ring and ball, the secondary graphite seal between seat ring and adapter, and seat ring and ball metal to metal contact reloaded by spring will minimize the internal process medium leakage.
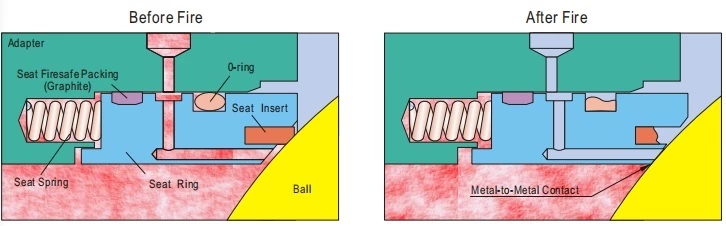
Fire Safe Design Trunnion Ball Valve with Secondary Metal to Metal Seat
External Leakage Prevention
The fire-resistant gasket and packings are used to provide fire-safe sealing to avoid external leakage.
Floating ball valve
For a fire safe design floating ball valve, all the possible external leakage points between stem and gland flange , gland flange and body, body and adapter are sealed with a 316+graphite gasket (part no. 8 in drawing), or graphite packing (part no. 12-14 in drawing). The graphite is fire-safe material which can prevent the process medium from leaking to the outside.
Trunnion ball valve
For a fire-safe trunnion ball valve, all the possible external leakage points between stem and gland flange , gland flange and body, body and adapter are sealed with a primary O-ring and a secondary graphite gasket. When fire burns out the primary O-ring seal, the secondary graphite gasket seal can still prevent the process medium from external leakage.
How To Make A Fire-Safe Test?
Test Procedure
Fire-safe tests determine the resistance of a fire-safe ball valve to a burn under controlled conditions as defined in common industry standards like: API 607, API 6 FA.
The performance requirements in these standards are meant to set what is acceptable for parts during a time period that is similar to how long it takes to put out most fires.
The complete fire test is performed in a steel-reinforced concrete bunker and is monitored from a safe distance. All relevant values are logged by our log and registration system.
The acceptance of the test results is based on how much the valve seat leaks from the inside and how much the valve leaks from the outside during the burn. The leakage from the inside and the leakage from the outside during the different steps of the test, both when it is hot and when it is cold, must not exceed the maximum values allowed by the standard.
Allowable Leakage Rate
Following the fire-safe test, the ball valve will be pressure tested. The allowable leakage rate is as shown in the below table.
Maximum Allowable Leakage Rate
| Through-seat Leakage | External Leakage | ||||||
| DN | NPS | During Burn | After Cool-down | During Burn and Cool-down | After Operational Test |
||
| Low Pressure Test | High Pressure Test | Low Pressure Test | Low Pressure Test | High Pressure Test | High Pressure Test |
||
| 8 | 1/4 | 32 | 128 | 13 | 8 | 32 | 8 |
| 10 | 3/8 | 40 | 160 | 16 | 10 | 40 | 10 |
| 15 | 1/2 | 60 | 240 | 24 | 15 | 60 | 15 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 80 | 320 | 32 | 20 | 80 | 20 |
| 25 | 1 | 100 | 400 | 40 | 25 | 100 | 25 |
| 32 | 1-1/4 | 128 | 512 | 51 | 32 | 128 | 32 |
| 40 | 1-1/2 | 160 | 640 | 64 | 40 | 160 | 40 |
| 50 | 2 | 200 | 800 | 80 | 50 | 200 | 50 |
| 65 | 2-1/2 | 260 | 1040 | 104 | 65 | 260 | 65 |
| 80 | 3 | 320 | 1280 | 128 | 80 | 320 | 80 |
| 100 | 4 | 400 | 1600 | 160 | 100 | 400 | 100 |
| 125 | 5 | 500 | 2000 | 200 | 125 | 500 | 125 |
| 150 | 6 | 600 | 2400 | 240 | 150 | 600 | 150 |
| 200 | 8 | 800 | 3200 | 320 | 200 | 800 | 200 |
| >200 | >8 | 800 | 3200 | 320 | 200 | 800 | 200 |
Note: All pressures in ml/min
Qualified Sizes
The qualified sizes are listed in the table below. For example, if a DN50 ball valve passes the fire safety test, then DN50 and below, DN65, 80, and 100 are qualified as fire-safe.
Valve Qualified by DN
| Size of Valve to be Tested DN | Other Valve Sizes Qualified DN |
| 50 | 50 and below; 65; 80; 100 |
| 65 | 65; 80; 100; 125 |
| 80 | 80; 100; 125; 150 |
| 100 | 100; 125; 150; 200 |
| 125 | 125; 150; 200; 250 |
| 150 | 150; 200; 250; 300 |
| 200 | 200 and larger |
Valve Qualified by NPS (Inch)
| Size of Valve to be Tested DN | Other Valve Sizes Qualified DN |
| 2 | 2 and below; 2-1/2; 3; 4 |
| 2-1/2 | 2-1/2; 3; 4; 5 |
| 3 | 3; 4; 5; 6 |
| 4 | 4; 5; 6; 8 |
| 5 | 5; 6; 8; 10 |
| 6 | 6; 8; 10; 12 |
| 8 | 8 and larger |
Valve Qualified by PN
| Valve Tested PN | Other Valves Qualified | |
| PN | Class Rating | |
| 10 | 10; 16 | 150 |
| 16 | 16; 25 | 150 |
| 25 | 25; 40 | 150; 300 |
| 40 | 40; 63; 100 | 300; 400; 600 |
| 63 | 63; 100 | 300; 400; 600 |
| 100 | 100; 150 | 600; 800; 900 |
| 150 | 150; 260 | 900; 1500 |
| 260 | 260; 420 | 1500; 2500 |
| 420 | 420 | 2500 |
Qualified Pressure
The qualified pressures are listed in the table below. For example, if a Class 150 ball valve passes the fire-safe test, then Class 150 and Class 300 ball valves are qualified as fire-safe.
Valve Qualified by Class
| Valve Tested Class | Other Valves Qualified | |
| Class Rating | PN | |
| 150 | 150; 300 | 10; 16; 25; 40 |
| 300 | 300; 400; 600 | 40; 63; 100 |
| 400 | 400; 600; 800 | 63; 100 |
| 600 | 600; 800; 900 | 63; 100 |
| 800 | 800; 900; 1500 | 100; 150; 260 |
| 900 | 900; 1500 | 150; 260 |
| 1500 | 1500; 2500 | 260; 420 |
| 2500 | 2500 | 420 |
What Are Fire-Safe Valve Standards?
API 607
API 607specifies fire type-testing requirements and a fire type-test method for confirming the pressure-containing capability of quarter-turn valves and other valves with nonmetallic seating under pressure during and after the fire test.
API 6FA
API 6FA standard establishes acceptable levels for leakage through the test valve and external leakage after exposure to a fire for a 30-minute time period. API 6FA standard establish the requirements for testing and evaluating the pressure-containing performance of API 6A and API 6D valves when exposed to fire.
What Fire Safe Certificates Does Relia Offer?
Relia Valve has sent the ball valves to TUV for fire-safe test. All the valves passed the test and we earned API 6FA and API 607 Certificates.
Relia API 6 FA Fire Safe Certificate for Ball Valve

Related Product:
8 inch ball valve, 26 inch ball valve, 28 inch ball valve, 30 inch ball valve




